The climate crisis calls for innovative solutions to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and improve energy efficiency. Systems to capture and store CO₂ before its release into the atmosphere or floating wind turbines that allow harnessing wind energy in deep waters are some of the sustainable and economically viable solutions developed by European companies.
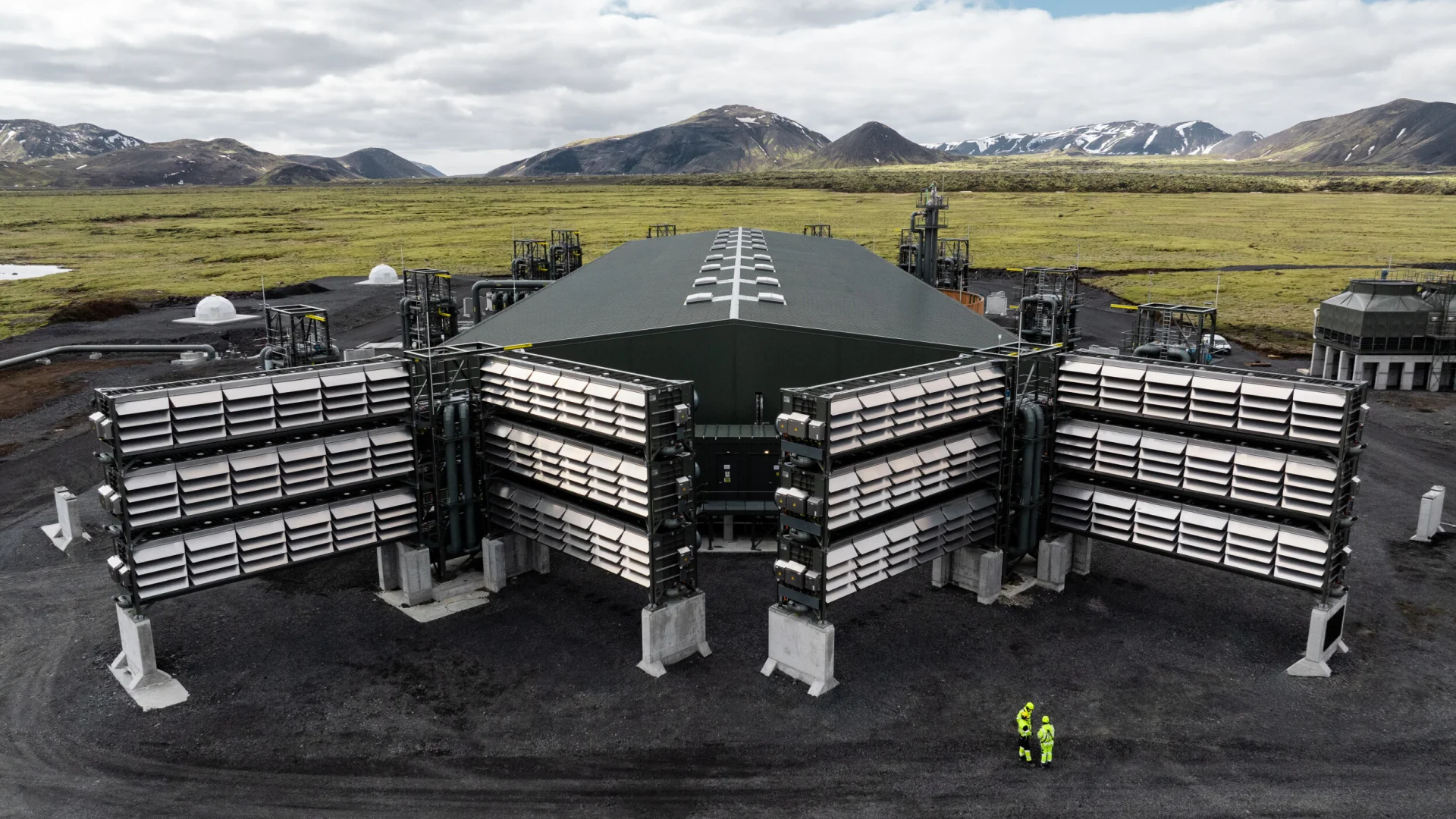

Mammoth (Iceland) commercial direct air capture and storage plant, developed by Climeworks. © Climeworks.
2. Floating wind turbines make it possible to harness wind energy in deep water, where currents are stronger and more constant. WindFloat Atlantic, a project of the Portuguese company EDP Renowables, has installed Europe’s first semi-submersible floating wind farm off the coast of Portugal, demonstrating its commercial viability.
3. Second-life batteries reduce the demand for critical raw materials such as lithium, cobalt and nickel, as well as reducing waste generation. In Spain, BeePlanet Factory reuses batteries from electric vehicles to convert them into energy storage systems for stationary applications, such as power grids and self-consumption in homes and industries.
4. Small Modular Reactors (SMRs) are smaller, modular and flexible, making them safer and more efficient than traditional reactors. The Italian company Newcleo is developing new-generation SMRs that use recycled fuel, which minimizes radioactive waste and improves the sustainability of nuclear energy.
5. Green hydrogen electrolyzers are essential for the decarbonization of the industrial and transportation sectors. H2B2, a company from Spain, designs and manufactures these devices, which produce hydrogen through the electrolysis of water using electricity from renewable sources, without generating CO₂ emissions.
6. Carbon capture technologies (CCUS) use chemical solvents to trap CO₂ generated in industrial processes. Carbon Clean, a UK company, has developed a system that can be integrated directly into cement plants to capture and store CO₂ before it is released into the atmosphere. Given that the cement industry is a major emitter of CO₂, this innovation represents a key breakthrough in emissions reduction.
7. Microgrids with storage are decentralized energy systems that allow homes and businesses to manage their energy consumption efficiently and autonomously. Ampere Energy, in Spain, offers intelligent solutions that optimize the use of renewable energy and reduce dependence on the conventional power grid.
8. Direct CO₂ capture from air (DAC) is a technology that extracts carbon dioxide directly from ambient air, using chemical or physical processes. Once captured, this CO₂ can be safely stored (e.g., underground in geological formations) or reused to produce synthetic fuels, carbonated beverages, building materials, etc. The Swiss company Climeworks has developed carbon capture plants in Europe that contribute to reducing greenhouse gas concentrations.
9. Sustainable biofuels for aviation and transportation, made from waste and used vegetable oils, can reduce CO₂ emissions by up to 80% compared to fossil fuels. Finnish company Neste produces biofuels and offers a more sustainable alternative for a sector that accounts for a considerable share of global emissions.
10. Passive radiative cooling takes advantage of the natural process of thermal radiation to cool surfaces without consuming energy. The technology works by reflecting heat back into outer space, which reduces the temperature of objects or buildings without the need for electricity. Cooling Photonics, in Spain, develops coatings that facilitate this process and contribute to the efficient cooling of buildings.